Why use our image compressor?
No Limits
Since the compression takes place directly in the browser, there are no restrictions on the number of images you can convert or the size of the images you can process.
100% Private
Images are compressed locally in your browser, which means your images are 100% safe and private.
Fast Compression
Just select your images and let our tool work its magic! In just seconds, you’ll have optimized images ready for your needs, saving you time and storage space.
See it in action
Our image compressor can reduce image file size up to 90% without losing quality. Check out the side-by-side comparison below, can you tell the difference?
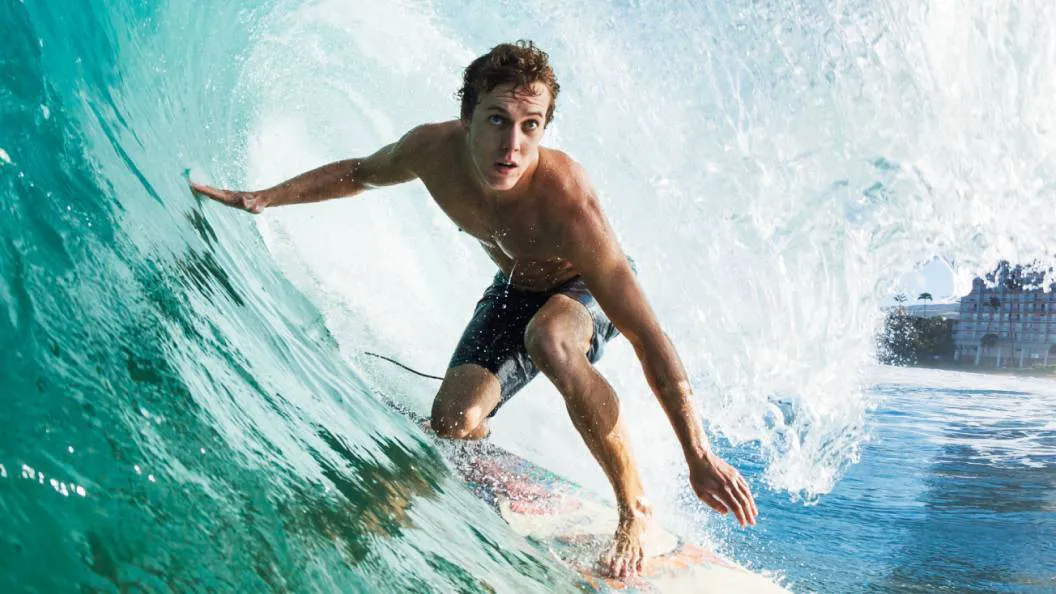
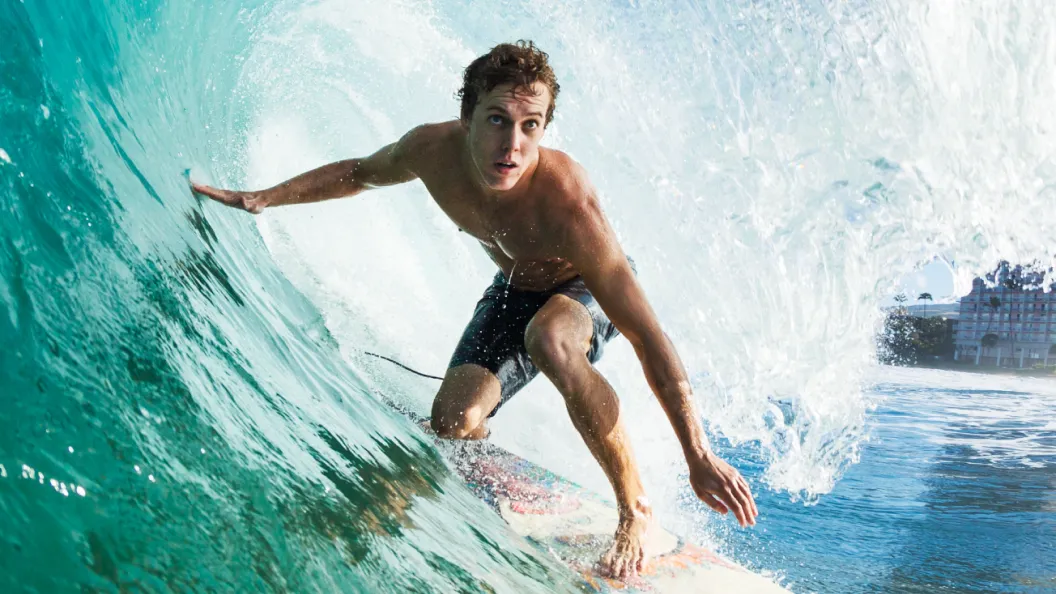


Which image format is right for you?
Check out the charts below to quickly find the best format for your needs
| Feature | JPG (JPEG) | PNG | WEBP | SVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Photos, realistic images | Logos, text, transparent backgrounds | Web images (photos & graphics) | Icons, logos, simple graphics |
| Compress Type | Lossy | Both lossy/lossless | Both lossy/lossless | Lossless |
| Image Quality | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Perfect (scalable) |
| File Size | ★ Small | Large | ★★ Very small | ★★★ Tiny (vector) |
| Transparency Support | ||||
| Animation Support | ||||
| Support on Browsers | All browsers | All browsers | Modern browsers (IE exceptions) | Modern browsers (IE limited) |
| Good for Printing? | Limited | |||
| Common Usage | Web images, digital photos, social media | Websites, logos, icons, web graphics | Modern websites, apps, and mobile | Logos, icons, illustrations, web design |
Pick Images to Compress
Why image compression and format choice matter?
Optimized image compression and format choices ensure faster loading, save bandwidth, and enhance user experience with high-quality visuals.
Faster Load Times
Compressed images reduce data transfer, enabling pages to load quickly and retain user engagement.
Improved User Experience (UX)
Fast-loading websites offer seamless browsing, boosting satisfaction and interaction.
Reduced Bandwidth Usage
Smaller image file sizes minimize data consumption, saving costs for high-traffic platforms.
SEO and Google Rankings
Optimized images boost loading speed, Core Web Vitals, SEO, Lighthouse scores, and user satisfaction.
Cost Efficiency
Efficient compression reduces hosting costs by lowering bandwidth for high-traffic sites.
Balancing Quality and Size
Choosing the right format (e.g., JPG, PNG, WebP) ensures high-quality visuals without unnecessary file size.
Ensuring Compatibility
Selecting formats compatible across devices and browsers guarantees consistent user experiences.
Optimizing for Mobile and Desktop
Mobile-first optimization demands efficient formats to support different screen sizes and network speeds.
Understanding image formats
JPEG (JPG) — Joint Photographic Experts Group
JPEG, also called JPG, is a type of image made up of tiny squares called pixels. It uses a method called “lossy compression,” which makes the file size smaller by removing some details. This makes it great for sharing pictures online.
JPG is very popular because it works with almost all websites, phones, and computers. Smaller file sizes mean pictures load faster and take up less space. Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram change your pictures to JPG to save space and make them load quickly while still looking good.

Pros of JPG
Small file size, fast loading.
Works on all browsers and devices.
Great for photos with rich colors.
Adjustable compression for quality vs. size.
Cons of JPG
Lossy compression reduces quality.
No transparency support.
Quality degrades with repeated edits.
Not ideal for sharp lines or text.
Why Our Tool Converts JPGs Progressively

Baseline loading
Delays can occur before the full image loads, making it feel slower.
Top-to-bottom loading is less engaging, especially for large images.
Baseline JPG images load progressively from top to bottom, displaying one line at a time. Users see the top portion of the image first, with additional sections appearing sequentially until the entire image is fully loaded.
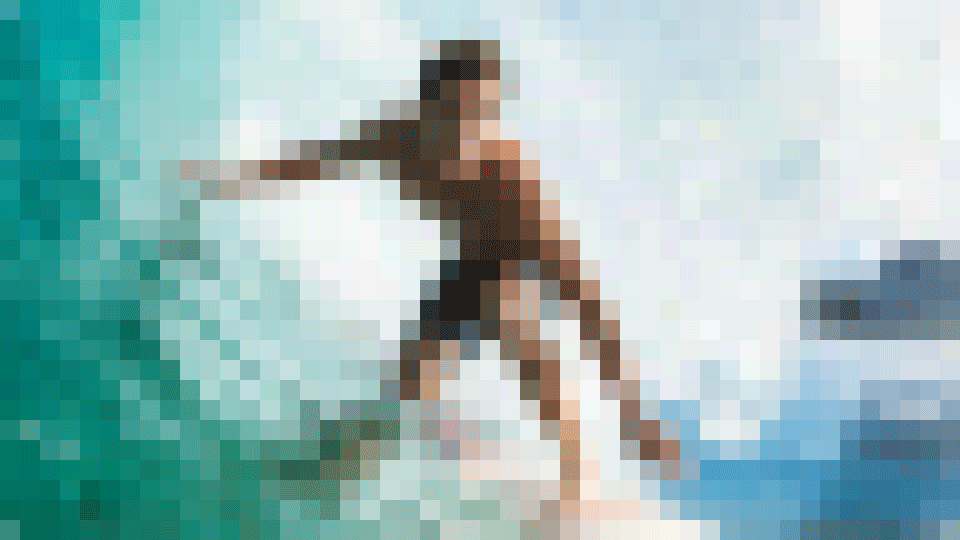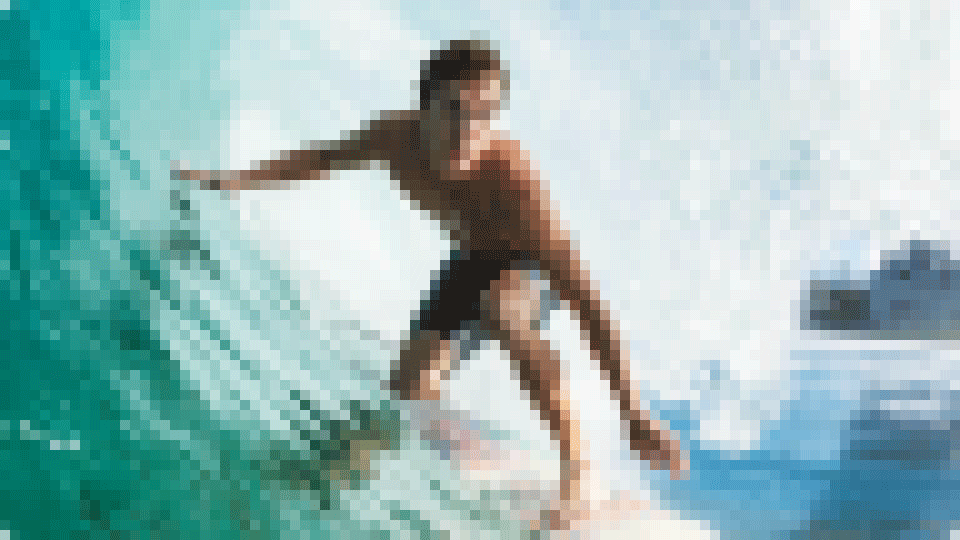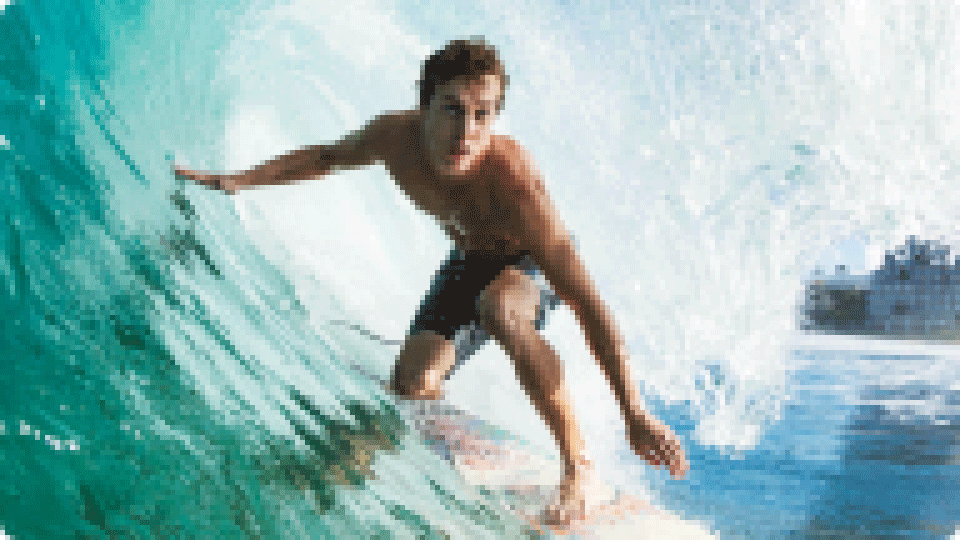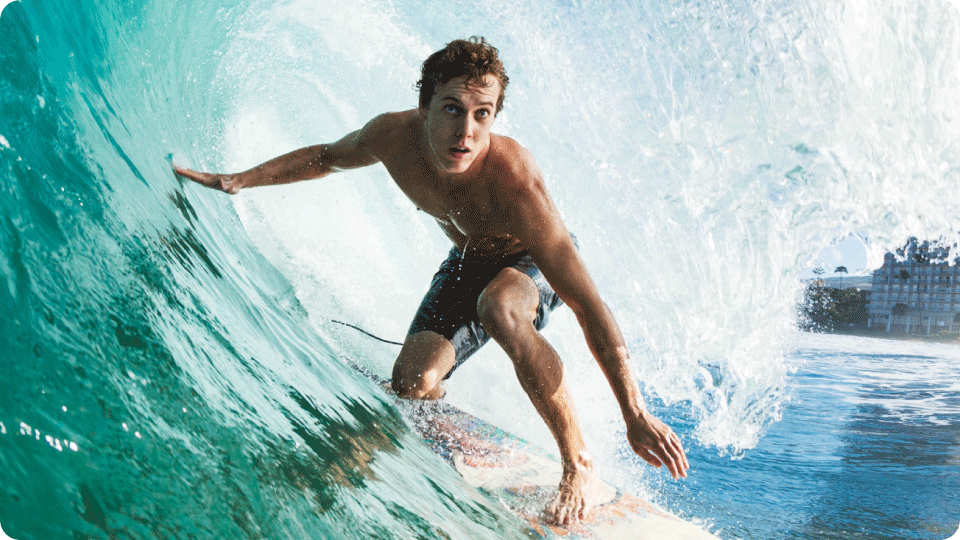
Progressive loading
Starts with a low-quality image that sharpens, feeling faster.
Immediate visual feedback keeps users engaged.
The progressive version of JPG starts by rendering a low-resolution preview of the image and gradually increases the level of details until the image reaches its original quality. Users can see the silhouettes of the objects right away, then the picture gets clearer as it loads.
PNG — Portable Network Graphics
PNG is an image format known for its lossless compression, meaning it preserves all image details even when the file size is reduced. Although PNG is a lossless format, there are some methods that can introduce a form of lossy compression, typically by reducing the image’s color depth or simplifying its palette.
PNG is perfect for pictures that include text, like posters or infographics, because the letters stay crisp. It also lets you use transparent backgrounds, which makes it great for designs and logos.

Pros of PNG
Lossless compression keeps quality intact.
Supports transparency (perfect for logos).
Crisp, high-quality images.
Fully compatible with all browsers.
Cons of PNG
Larger file size slows loading.
Not ideal for photos.
Can impact website performance.
WEBP – Web Optimized Picture
WebP is a newer image format that works better than JPG and PNG in many ways. It can shrink the size of a picture a lot without making it look worse. WebP can use both lossy and lossless compression, so it’s flexible.
Switching to WebP helps websites save storage space and use less internet data. This format can even handle animations and see-through backgrounds, making it a great choice for modern websites.

Pros of WebP
Smaller file size, good quality.
Supports transparency and animation.
Better quality than JPG at smaller sizes.
Cons of WebP
Limited browser support (older versions).
Needs fallback formats for compatibility.
Less widely used than JPG/PNG.
SVG – Scalable Vector Graphics
SVG, which stands for Scalable Vector Graphics, is a format for making pictures that can be resized without losing quality. Unlike JPG or PNG, SVG isn’t made of pixels. Instead, it uses math to draw shapes and lines.
This format is perfect for icons, charts, and designs that need to look good at any size. You can also change SVG images easily with design tools, or even by using code. That’s why it’s a favorite for creating interactive graphics on websites.

Pros of SVG
Scalable without losing quality.
Small file size for simple graphics.
Supports transparency.
Can be edited with code.
Cons of SVG
Not for photos or complex images.
Limited support in older browsers.
Can get large if too detailed.
Pick Images to Compress